

Out of Stock




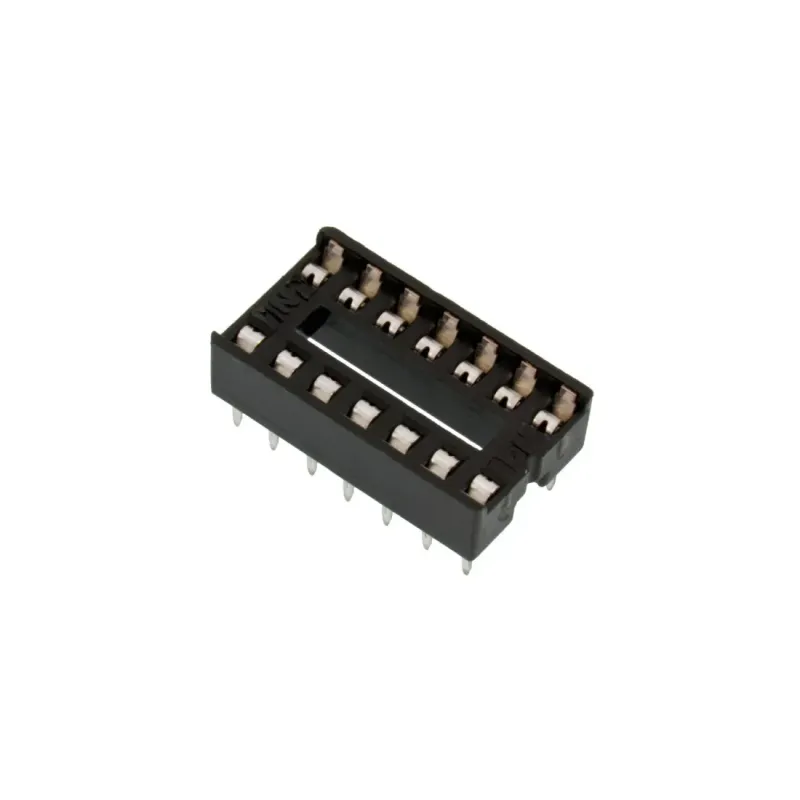
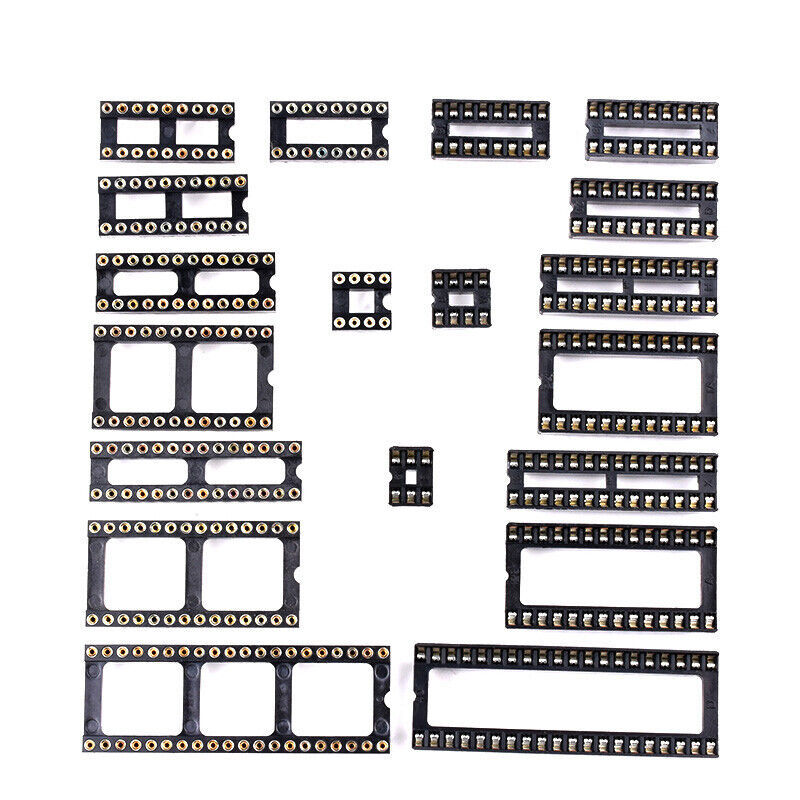
IC Socket 2x7 - DIP 14-Pin Integrated Circuit
0.65RON
- Stock: Out of Stock
- Model: ICCXXX.DIP14P
Your orders placed until 16:30 on weekdays are shipped on the same day.
2x7 IC - Integrated Circuit Socket 14 Pins DIP-14
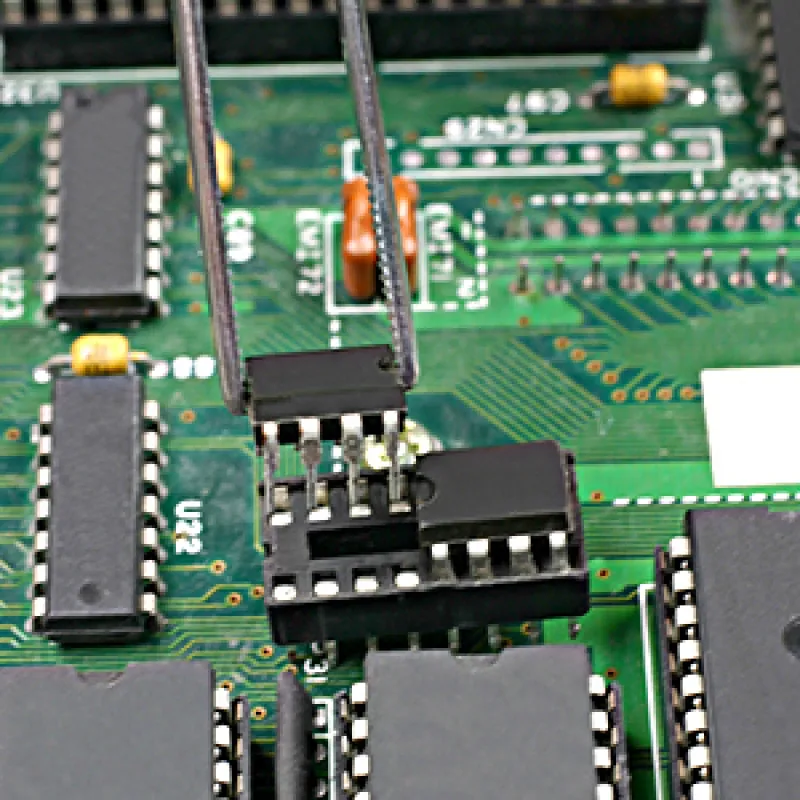
Integrated Circuit (IC) sockets function as connectors that facilitate the easy insertion and removal of ICs from a printed circuit board (PCB). They offer a convenient method of mounting ICs without the need for soldering them directly onto the PCB. This feature is particularly advantageous during prototyping, testing, and repair stages.
Key Features
- Ease of Use: ICs can be conveniently inserted and removed, making them perfect for prototyping and testing.
- Protection: They offer protection to ICs from potential heat damage during the soldering process.
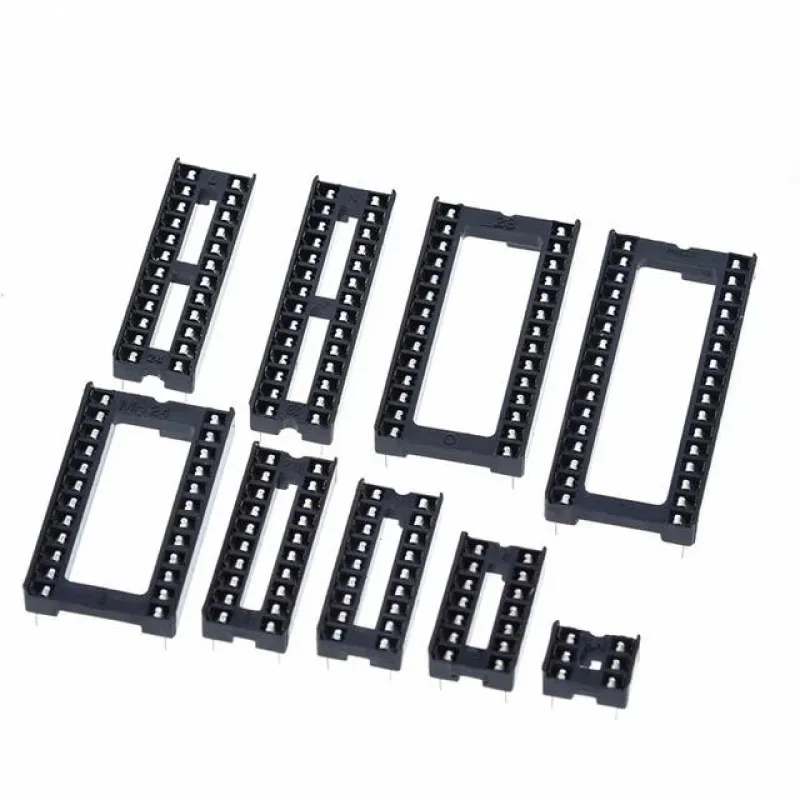
- Versatility: They come in a range of sizes and configurations to suit different IC packages.
- Reusability: IC sockets can be reused, allowing for straightforward replacement of ICs without the need for desoldering.
Types of IC Sockets
- DIP (Dual In-Line Package) Sockets: Designed for ICs with two parallel rows of pins. Commonly used in prototyping and development boards and come in pin counts of 8, 14, 16, 20, 24, 28, 40, and so on.
- SIP (Single In-Line Package) Sockets: Used for ICs with a single row of pins and are less common, typically used for specific types of ICs or modules.
- ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) Sockets: Allow for the insertion and removal of ICs without any insertion force. Ideal for testing and programming where frequent IC changes are required.
- PLCC (Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier) Sockets: Designed for PLCC IC packages, which have leads on all four sides. Commonly used in applications requiring high pin counts and come in pin counts of 20, 28, 32, 44, 52, 68, and so on.
- BGA (Ball Grid Array) Sockets: Used for ICs with an array of solder balls on the bottom. Used in high-density, high-performance applications like CPUs and GPUs.
- PGA (Pin Grid Array) Sockets: Used for ICs with an array of pins arranged in a grid pattern. Common in older CPU sockets and some high-power applications.
Advantages of Using IC Sockets
- Flexibility: They allow for easy swapping of ICs for testing or upgrading.
- Damage Prevention: They protect ICs from thermal stress and potential damage during soldering.
- Maintenance: They facilitate easy replacement of faulty ICs without the need for desoldering.
- Prototyping: They are essential in development and prototyping environments where ICs may need frequent replacement.
Disadvantages
- Additional Cost: They add to the overall cost of the PCB design.
- Increased Height: They add to the height of the PCB, which may be a concern in compact designs.
- Potential for Poor Contact: Over time, contacts in the socket can wear out or become unreliable.
Applications
- Prototyping and Development: They allow for easy swapping of ICs during the design and testing phases.
- Repair and Maintenance: They facilitate easy replacement of faulty ICs in electronic devices.
- Educational Kits: They are used in educational kits and development boards for their ease of use and versatility.
- Production: In some cases, they are used in low-volume production where frequent updates or changes are anticipated.
Conclusion
IC sockets are essential components in the electronics industry, offering flexibility, protection, and convenience. They are indispensable in prototyping, testing, and situations that require frequent replacement of ICs. Despite the additional cost and increased height, the benefits they provide often outweigh the disadvantages, making them a popular choice in various applications.
Package Includes
1 x IC Socket 2x7















