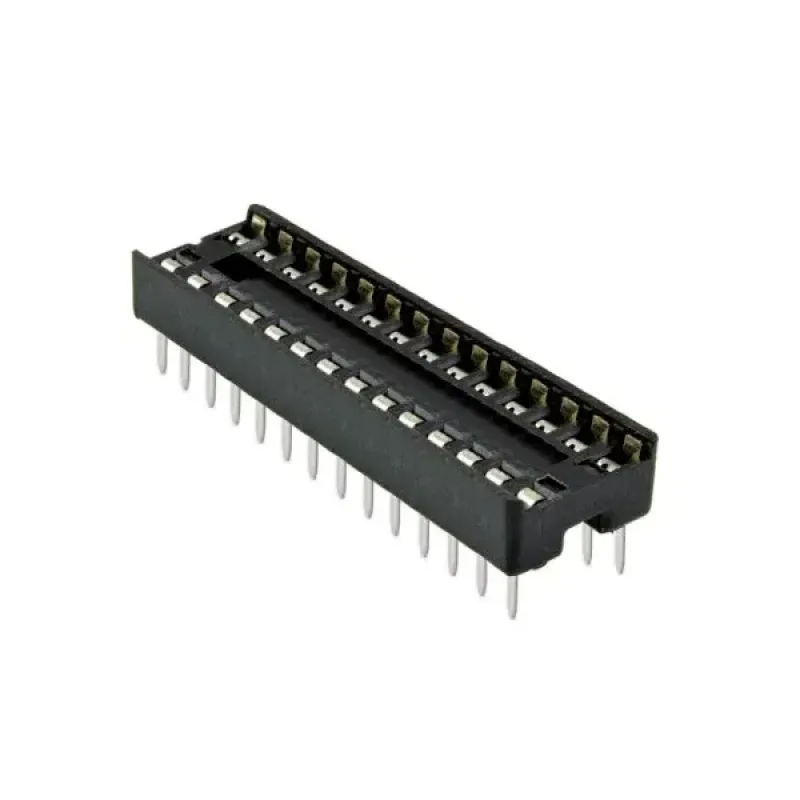





IC Socket 2x14 - DIP 28-Pin Integrated Circuit
71.46RON
- Stock: In Stock
- Model: ICCXXX.DIP28
Your orders placed until 16:30 on weekdays are shipped on the same day.
2x14 Integrated Circuit - IC Socket 28 Pins DIP-28
Integrated Circuit (IC) sockets serve as connectors that facilitate the easy insertion and removal of ICs from a printed circuit board (PCB). They offer a method of mounting ICs without the need for direct soldering onto the PCB. This feature is particularly advantageous during prototyping, testing, and repair processes.
Key Characteristics:
- Ease of Use: ICs can be effortlessly inserted and removed, making them perfect for prototyping and testing.
- Protection: They aid in shielding ICs from heat damage during soldering.
- Versatility: They come in a range of sizes and configurations to suit different IC packages.
- Reusability: IC sockets can be reused, enabling easy replacement of ICs without desoldering.
Varieties of IC Sockets:
- DIP (Dual In-Line Package) Sockets: Designed for ICs with two parallel rows of pins. Common pin counts include 8, 14, 16, 20, 24, 28, 40, etc. Widely used in prototyping and development boards.
- SIP (Single In-Line Package) Sockets: Intended for ICs with a single row of pins. Less common, used for specific types of ICs or modules.
- ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) Sockets: Allow ICs to be inserted and removed without any insertion force, using a lever or cam mechanism. Ideal for testing and programming where frequent IC changes are required.
- PLCC (Plastic Leaded Chip Carrier) Sockets: Designed for PLCC IC packages with leads on all four sides. Common pin counts include 20, 28, 32, 44, 52, 68, etc. Used in applications requiring high pin counts.
- BGA (Ball Grid Array) Sockets: Intended for ICs with an array of solder balls on the bottom. Used in high-density, high-performance applications like CPUs and GPUs.
- PGA (Pin Grid Array) Sockets: Designed for ICs with an array of pins arranged in a grid pattern. Common in older CPU sockets and some high-power applications.
Benefits of Using IC Sockets:
- Flexibility: Allow for easy swapping of ICs for testing or upgrading.
- Damage Prevention: Protect ICs from thermal stress and potential damage during soldering.
- Maintenance: Facilitate easy replacement of faulty ICs without desoldering.
- Prototyping: Crucial in development and prototyping environments where ICs may need frequent replacement.
Drawbacks:
- Additional Cost: Add to the cost of the PCB design.
- Increased Height: Add height to the PCB, which may be a concern in compact designs.
- Potential for Poor Contact: Over time, contacts in the socket can wear out or become unreliable.
Applications:
- Prototyping and Development: Allow for easy swapping of ICs during the design and testing phases.
- Repair and Maintenance: Facilitate easy replacement of faulty ICs in electronic devices.
- Educational Kits: Used in educational kits and development boards for ease of use and versatility.
- Production: In some cases, used in low-volume production where frequent updates or changes are expected.
Conclusion:
IC sockets are indispensable components in electronics, offering flexibility, protection, and user-friendliness. They are vital in prototyping, testing, and situations where frequent IC replacement is necessary. Despite the additional cost and increased height, their benefits often surpass the drawbacks, making them a preferred choice in various applications.
Package Includes:
1 x IC Socket 2x14















